- Hacked Gadgets: A resource for DIY project documentation as well as general gadget and technology news.
- HackRead: HackRead is a News Platform that centers on InfoSec, Cyber Crime, Privacy, Surveillance, and Hacking News with full-scale reviews on Social Media Platforms.
- The Hacker News: The Hacker News — most trusted and widely-acknowledged online cyber security news magazine with in-depth technical coverage for cybersecurity.
- Phrack Magazine: Digital hacking magazine.
- KitPloit: Leading source of Security Tools, Hacking Tools, CyberSecurity and Network Security.
- SecTools.Org: List of 75 security tools based on a 2003 vote by hackers.
- Hakin9: E-magazine offering in-depth looks at both attack and defense techniques and concentrates on difficult technical issues.
- Metasploit: Find security issues, verify vulnerability mitigations & manage security assessments with Metasploit. Get the worlds best penetration testing software now.
- SecurityFocus: Provides security information to all members of the security community, from end users, security hobbyists and network administrators to security consultants, IT Managers, CIOs and CSOs.
- Packet Storm: Information Security Services, News, Files, Tools, Exploits, Advisories and Whitepapers.
- Exploit DB: An archive of exploits and vulnerable software by Offensive Security. The site collects exploits from submissions and mailing lists and concentrates them in a single database.
- NFOHump: Offers up-to-date .NFO files and reviews on the latest pirate software releases.
Is an open source tool to help you build a valid SSL certificate chain from the root certificate to the end-user certificate. Also can help you fix the incomplete certificate chain and download all missing CA certificates.
How To Use
It's simple:
# Clone this repository
git clone https://github.com/trimstray/sslmerge
# Go into the repository
cd sslmerge
# Install
./setup.sh install
# Run the app
sslmerge -i /data/certs -o /data/certs/chain.crt
- symlink to
bin/sslmergeis placed in/usr/local/bin- man page is placed in
/usr/local/man/man8
Parameters
Provides the following options:
Usage:
sslmerge <option|long-option>
Examples:
sslmerge --in Root.crt --in Intermediate1.crt --in Server.crt --out bundle_chain_certs.crt
sslmerge --in /tmp/certs --out bundle_chain_certs.crt --with-root
sslmerge -i Server.crt -o bundle_chain_certs.crt
Options:
--help show this message
--debug displays information on the screen (debug mode)
-i, --in add certificates to merge (certificate file, multiple files or directory with ssl certificates)
-o, --out saves the result (chain) to file
--with-root add root certificate to the certificate chainHow it works
Let's start with ssllabs certificate chain. They are delivered together with the sslmerge and can be found in the
example/ssllabs.com directory which additionally contains the all directory (containing all the certificates needed to assemble the chain) and the server_certificate directory (containing only the server certificate).The correct chain for the ssllabs.com domain (the result of the openssl command):
Certificate chain
0 s:/C=US/ST=California/L=Redwood City/O=Qualys, Inc./CN=ssllabs.com
i:/C=US/O=Entrust, Inc./OU=See www.entrust.net/legal-terms/OU=(c) 2012 Entrust, Inc. - for authorized use only/CN=Entrust Certification Authority - L1K
1 s:/C=US/O=Entrust, Inc./OU=See www.entrust.net/legal-terms/OU=(c) 2012 Entrust, Inc. - for authorized use only/CN=Entrust Certification Authority - L1K
i:/C=US/O=Entrust, Inc./OU=See www.entrust.net/legal-terms/OU=(c) 2009 Entrust, Inc. - for authorized use only/CN=Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2
2 s:/C=US/O=Entrust, Inc./OU=See www.entrust.net/legal-terms/OU=(c) 2009 Entrust, Inc. - for authorized use only/CN=Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2
i:/C=US/O=Entrust, Inc./OU=www.entrust.net/CPS is incorporated by reference/OU=(c) 2006 Entrust, Inc./CN=Entrust Root Certification Authority- Identity Certificate (Server Certificate)
issued for ssllabs.com by Entrust Certification Authority - L1K
- Intermediate Certificate
issued for Entrust Certification Authority - L1K by Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2
- Intermediate Certificate
issued for Entrust Root Certification Authority - G2 by Entrust Root Certification Authority
- Root Certificate (Self-Signed Certificate)
issued for Entrust Root Certification Authority by Entrust Root Certification Authority
Scenario 1
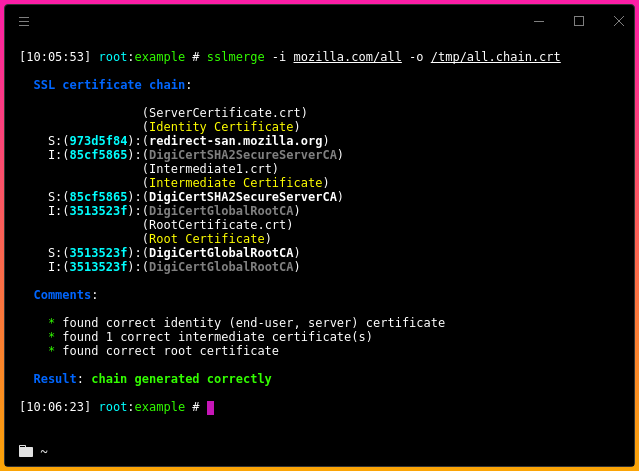
In this scenario, we will chain all delivered certificates. Example of running the tool:
Scenario 2
In this scenario, we only use the server certificate and use it to retrieve the remaining required certificates. Then, as above, we will combine all the provided certificates. Example of running the tool:
Certificate chain
In order to create a valid chain, you must provide the tool with all the necessary certificates. It will be:
- Server Certificate
- Intermediate CAs and Root CAs
However, if you look inside the generated chain after generating with sslmerge, you will not find the root certificate there. Why?
Because self-signed root certificates need not/should not be included in web server configuration. They serve no purpose (clients will always ignore them) and they incur a slight performance (latency) penalty because they increase the size of the SSL handshake.
If you want to add a root certificate to the certificate chain, call the utility with the
--with-root parameter.Certification Paths
Sslmerge allows use of two certification paths:
Output comments
When generating the chain of certificates, sslmerge displays comments with information about certificates, including any errors.
Here is a list of all possibilities:
not found identity (end-user, server) certificate
The message is displayed in the absence of a server certificate that is the beginning of the chain. This is a unique case because in this situation the sslmerge ends its operation displaying only this information. The server certificate is the only certificate required to correctly create a chain. Without this certificate, the correct chain will not be created.
found correct identity (end-user, server) certificate
The reverse situation here - message displayed when a valid server certificate is found.
not found first intermediate certificate
This message appears when the first of the two intermediate certificates is not found. This information does not explicitly specify the absence of a second intermediate certificate and on the other hand it allows to determine whether the intermediate certificate to which the server certificate was signed exists. Additionally, it can be displayed if the second intermediate certificate has been delivered.
not found second intermediate certificate
Similar to the above, however, it concerns the second intermediate certificate. However, it is possible to create the chain correctly using the second certification path, e.g. using the first intermediate certificate and replacing the second with the main certificate.
one or more intermediate certificate not found
This message means that one or all of the required intermediate certificates are missing and displayed in the absence of the root certificate.
found 'n' correct intermediate certificate(s)
This message indicates the number of valid intermediate certificates.
not found correct root certificate
The lack of the root certificate is treated as a warning. Of course, when configuring certificates on the server side, it is not recommended to attach a root certificate, but if you create it with the sslmerge, it treats the chain as incomplete displaying information about the incorrect creation of the chain.
an empty CN field was found in one of the certificates
This message does not inform about the error and about the lack of the CN field what can happen with some certificates (look at
example/google.com). Common Name field identifies the host name associated with the certificate. There is no requirement in RFC3280 for an Issuer DN to have a CN. Most CAs do include a CN in the Issuer DN, but some don't, such as this Equifax CA.Requirements
Sslmerge uses external utilities to be installed before running:
Other
Contributing
See this.
Project architecture
See this.